解决: Mysql安装时mysqld.exe报`应用程序无法正常启动(0xc000007b)`的问题
本文共 205 字,大约阅读时间需要 1 分钟。
问题情况:
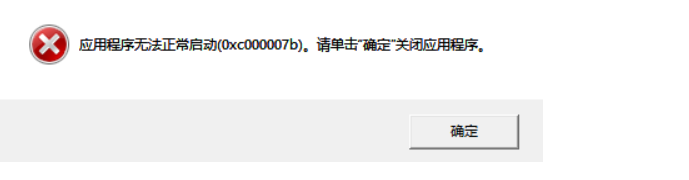 解决方案: 下载一个修复工具,这里附上修复工具链接: 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1HxKLkd0NIgiQ5x1_BaI0_Q 提取码:p1a8 1.下载工具后解压, 2.以管理员身份运行DirectX Repair.exe文件 3.工具=>选项=>扩展 | 点击开始扩展
解决方案: 下载一个修复工具,这里附上修复工具链接: 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1HxKLkd0NIgiQ5x1_BaI0_Q 提取码:p1a8 1.下载工具后解压, 2.以管理员身份运行DirectX Repair.exe文件 3.工具=>选项=>扩展 | 点击开始扩展 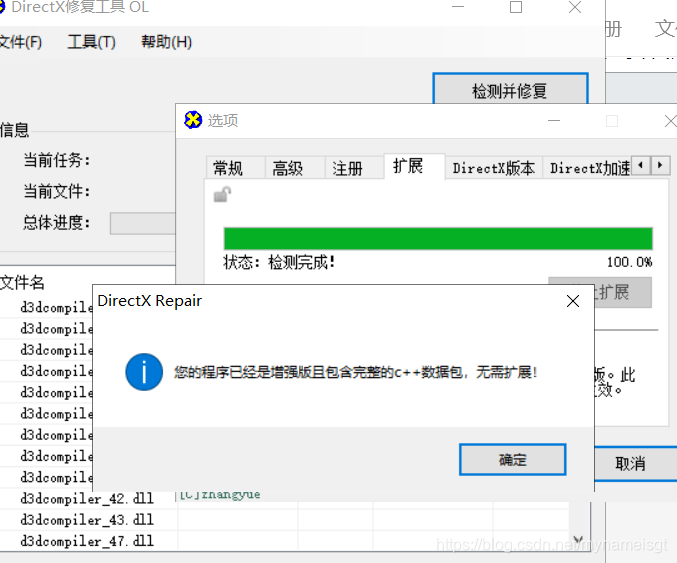 4.工具=>选项=>高级 | 点击确定
4.工具=>选项=>高级 | 点击确定 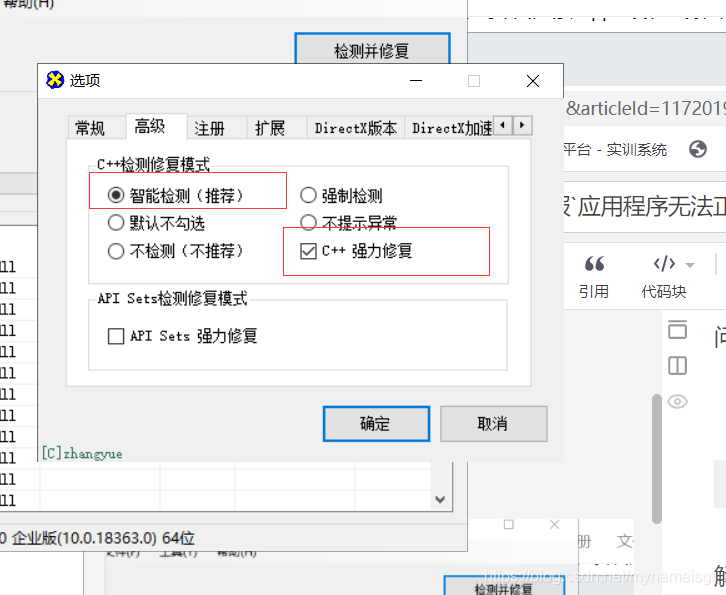 5.回到主页|点击检测并修复
5.回到主页|点击检测并修复 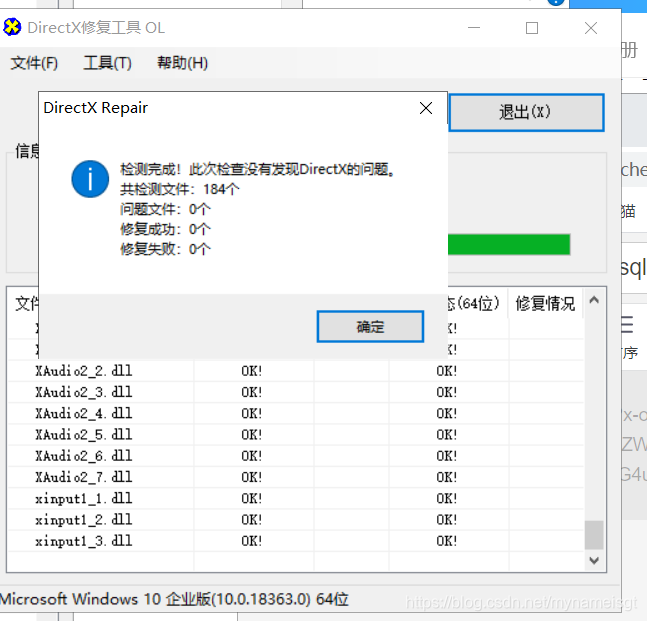 6.此时就消除报错了!!!
6.此时就消除报错了!!! 转载地址:http://esxwk.baihongyu.com/
你可能感兴趣的文章